What are product variations
Variations (also known as parent-child relationships) are sets of products that are related to one another in terms of size or flavor, and so on. Good variation relationship listings allow customers to compare and choose products based on different attributes such as size, or other characteristics from the available options on a single product detail page. For example, a customer searching for a short sleeved T-shirt might click a product detail page for a T-shirt that comes in four sizes (small, medium, large and extra-large). Rather than having to browse separate pages for each size, the customer can select the preferred size variations on the same page.
Examples of good variation families are:
- Items of clothing that come in different sizes (small, medium, large)
Variation requirements
If your products fulfill the following requirements, typically they are good candidates for a variation:
- The products are fundamentally the same.
- The products are under the same brand name.
- The products vary only in a few very specific ways.
- Buyers expect to find these products together on a single product page.
- Products could share a single title.
GUIDE ON THE CORRECT USE OF THE VARIATION FIELD
This guide will help you use the variation field correctly to avoid rejections during quality
control.
The variation field is visible on the website (next to the product/images). It is essential to enter a
variation
only in the cases mentioned below.
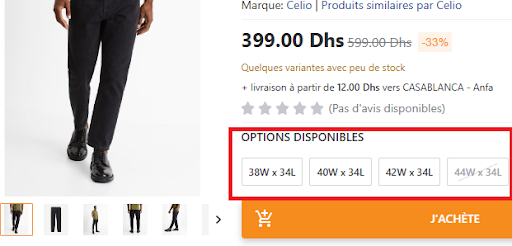
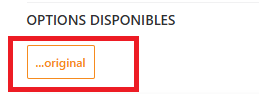
Categories with Predefined Variations
For products in the following categories, choose the appropriate variation from the dropdown
list:
● Clothing
● Shoes
● Lingerie
● Perfumes
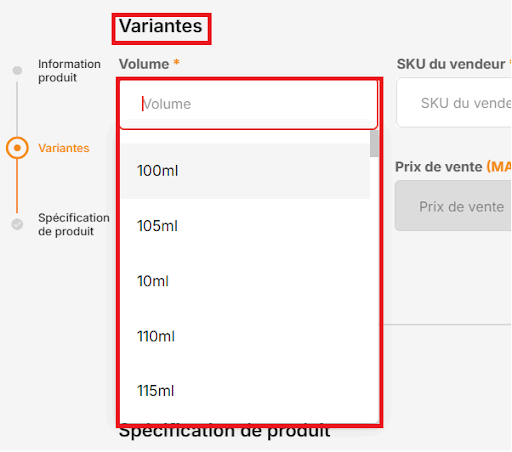
Categories with Free-Text Variations
For other categories, you must manually input the variation in the free-text space.
Examples of Allowed Variations:
● Clothing sizes (e.g., S, M, L)
● Shoe sizes (e.g., 37, 38, 39, 40)
● Product volume (e.g., L, cl, ml)
● Product weight (e.g., g, kg)
● Product dimensions (L x W x H in cm)
● Screen size
● Power
● Storage
● Capacity
If none of the above are applicable, fill in the field with three dots (…) to indicate that no
variation is available.
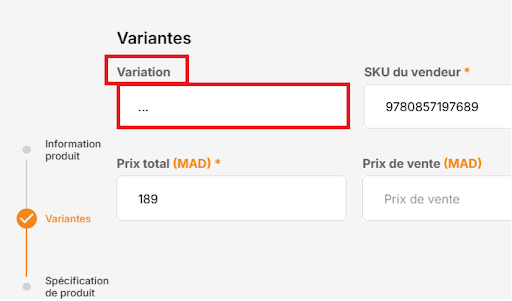
What You Should Not Do
● Avoid random text, product names, or descriptions in the variation field.
● Even if the free-text field allows it, the product will be rejected during quality control.
Variation Requirements
For products to be eligible for variation, the following criteria must be met:
1. Products are fundamentally the same.
2. Products belong to the same brand.
3. Products differ only based on specific criteria.
4. Customers expect to find these products grouped on the same product page.
5. Products can share a unique title.
When to Use or Not Use Variations
Ask yourself these questions to determine if products can be considered valid variations:
● Are the products fundamentally the same?
● Can the products share the same title?
● Do the products vary only based on specific criteria that do not alter their nature (e.g.,
size)?
● Do customers expect to see these products grouped together on the same product
page?
Products Not Suitable for Variations
● There is only one variation of the product.
● Products have a different appearance that requires distinct images.
● Products are fundamentally different.
● Products belong to different brands.
● Product descriptions are very different.
● Products cannot share a unique title.
● Customers would not expect these products to appear on the same product page.
How to Add Product Variations
1. Add the value of the corresponding attribute for each variation in the “Variation” column
(e.g., S, M, L).
2. Fill in the “SellerSKU” and “gtin_barcode” fields for each variation.Important Note:
● Jumia systems support only one variation. Products must vary based on one criterion
only (e.g., size, but not both size and color).
● Submit one set of common images for all product variations.
● Since images do not change when a variation is selected, the type of variation must be
an attribute that does not affect the external appearance of the product (images).
Examples of Attributes Allowed for Variations:
● Size, power, storage, capacity, etc.
Examples of Attributes NOT Allowed for Variations:
● Color, shape, etc.
Best Practices
1. Do not group different products together:
○ Example 1: A phone charging cable and a portable charger, although related, are
not the same product and must be listed separately.
○ Example 2: A laptop bag with handles and one without handles are two different
product styles and must be listed on separate product pages.
2. Do not misuse variation themes:
○ Themes must be used only for their intended purpose.
○ For example, a size-based variation theme should include only size-related
information.
○ Different phone models must not be listed under a size theme.
For any questions, please contact the support team.
When to use or not to use variation relationships
The following questions can help you to determine whether certain products are valid variations:
- Are the products fundamentally the same?
- Can products share the same title?
- Do the products vary only in a few, specific ways that do not alter the core essence and nature of the item (such as size)?
- Would customers expect to find these products together on a single product detail page?
The following describe a product that is Not a good candidate for variation:
- There is only one variation of your product.
- The products look different and would require different images to be displayed accurately
- The products are fundamentally different.
- The products have different brand name.
- Products require very different product descriptions.
- Products cannot be described by a single product title.
- A customer would not expect to find the products together on the product page.
How to add product variations
Add the attribute value related to each variation in the variation column (ex: S, M, L), fill the Seller SKU and gtin_barcode for each variation.
Jumia systems only supports single variation. The product should vary by only one criteria (ex: size variation only, but not size and color).
You can submit only one set of images that will be common to all product variation.
Since images don’t change when selecting a variation, variation type can be any attribute that does not impact the external product appearance (images).
- Examples of attributes that CAN as variations: size, power, storage, capacity, etc.
- Examples of attributes that can NOT be used as variation: color, shape, etc.
Best practices
- Do not list different products together:
- Example 1: A mobile phone charging cable and a portable charger, while related, are not the same product and should not be listed on the same detail page.
- Example 2: A laptop bag with handles and a laptop bag without handles are two different product styles that should be listed on separate detail pages.
- Do not use variation themes incorrectly, they should only be used for their defined purpose.
- For example: A size variation theme must not include any information other than size. Different phone models, for example, should not be listed within a size theme.










